Types of Sewage Treatment Plants Installed
There are four basic types of sewage treatment plants.
| Activated Sludge Plants | 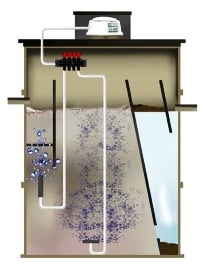 | Examples WPL Diamond Conder ASP Bio Pure Biodigester |
| Submerged Aerated Filters |  | Examples Valance Tricel
|
| Biodiscs |  | Examples |
| Fliter Systems |  | Examples Biorock Filterpod |
Activated Sludge Plants
This type of plant has replaced many submerged aerated filter models.
Activated Sludge Technology uses two stages of dealing with commerical and residential sewage / waste water:
- They have no primary settlement tanks.
- Secondary Treatment The sewage flows straight to the digestion chamber or 'Biozone', where the organic material in the sewage is digested. The Activated Sludge process is a natural biological treatment process, involving many different sorts of bugs. In the Activated Sludge Plant (ASP) bacteria produce sticky substances that coat the bits of organic material in the sewage. The particles stick together to form lumps or 'flocs', creating a structure within which the bugs live. The milk chocolate coloured activated sludge is aerated to dissolve oxygen in the sewage liqor, which allows the bacteria to breathe and the organic matter (BOD) to be digested by the bugs.
- Final Settlement / Clarification The sewage effluent then flows to a clarification chamber, where the flocs sink to the bottom and are transferred back to the digestion chamber.
The tank should be big enough to allow sufficient contact time (retention time) between the sewage and the activated sludge for all the digestion to take place.
Submerged Aerated Filters
These plants became popular in the 1990's.
Submerged Aerated Filter technology uses three stages of dealing with commerical and residential sewage / waste water:
- Primary Settlement Larger solids settle into the bottom of the primary tank and buoyant material float to the top to form a crust. These are both removed periodically by tanker.
- Secondary Treatment Suspended solids, floating in the liquor, transfer to the Biozone for digestion by the bugs. The air required by the bugs to breathe is supplied by a blower that bubbles air through the chamber. The chamber is also filled with media - usually plastic shapes with a lot of surface area for the bugs to grow on and attach to.
- Final Settlement / Clarification Where remaining solids and dead bacteria (Humus) are settled out of the biological treated effluent.
Biodiscs
These are the original sewage treatment plant designed in the 1970's.
Biodisc technology uses three stages of dealing with commerical and residential sewage / waste water:
- Primary Settlement Larger solids settle into the bottom of the primary tank and buoyant material float to the top to form a crust. These are both removed periodically by tanker.
- Secondary Treatment Suspended solids, floating in the liquor, transfer to the Biozone for digestion by the bugs. The biozone has within it a compact series of rotating discs, driven by an internal motor and gearbox, which continually turns the discs. The bugs grow on the discs and breathe as the discs turn out of the sewage and into the air, so the sequence is 'Breathe, Eat, Breathe, Eat'.
- Final Settlement / Clarification Where remaining solids and dead bacteria (Humus) are settled out of the biological treated effluent.
Filter Systems
Filter System technology uses two stages of dealing with commerical and residential sewage / waste water:
- Primary Settlement Larger solids settle into the bottom of the primary tank and buoyant material float to the top to form a crust. These are both removed periodically by tanker.
- Secondary Treatment Suspended solids, floating in the liquor, transfer to the Biozone for digestion by the bugs. The biozone has within it a physical filter, either peat, rockwool or coco-fibre, which filters and traps the suspended solids. The bugs grow within the filter media and digest them. The final effluent is clean when it leves the filter and is discharged to the environment without the need for clarification.
